Physio Meets Science on Twitter: "The anti-inflammatory effects of exercise: mechanisms and implications for the prevention and treatment of disease. https://t.co/nAHikk2RPt https://t.co/VqHUhotOHW" / Twitter
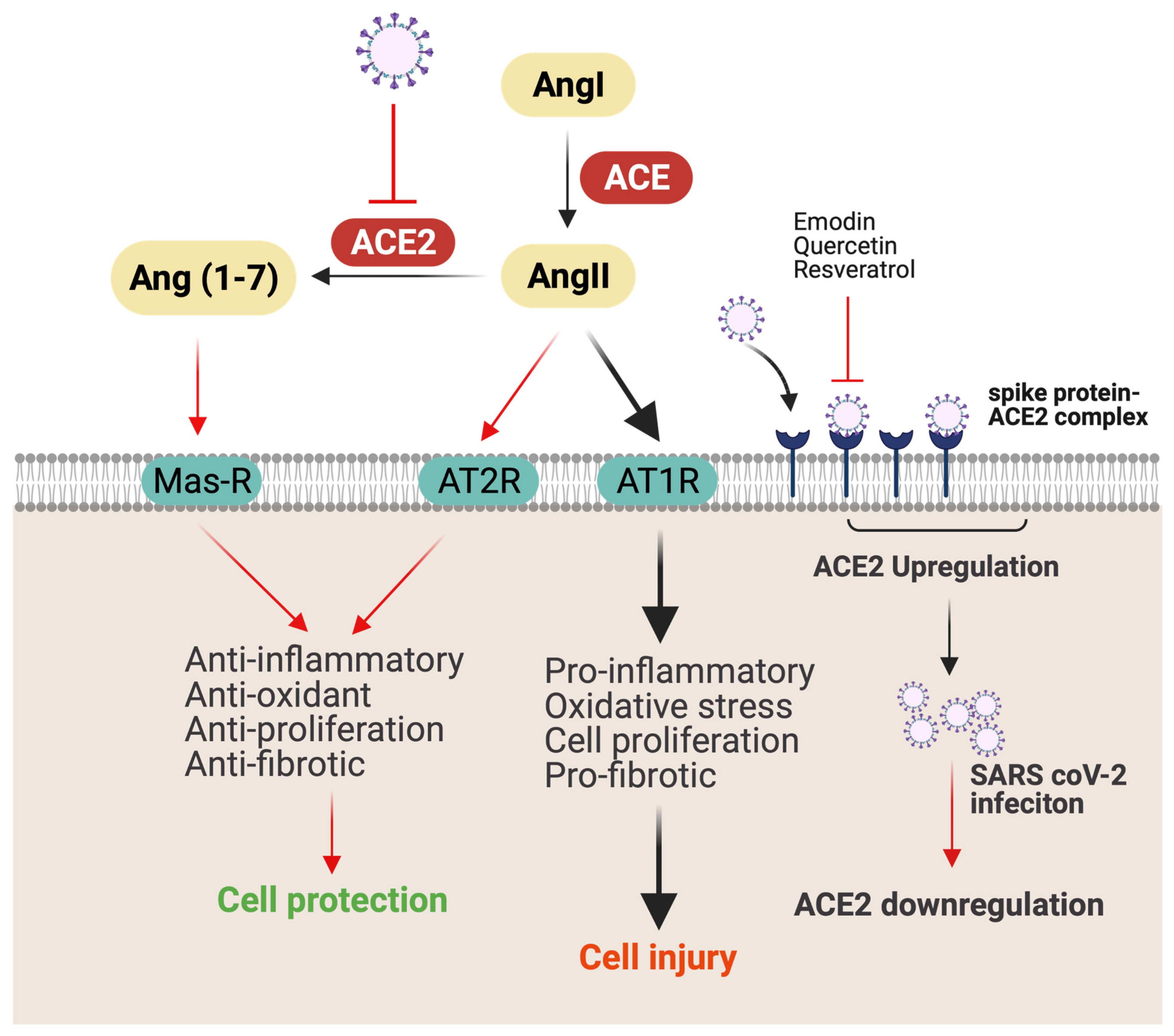
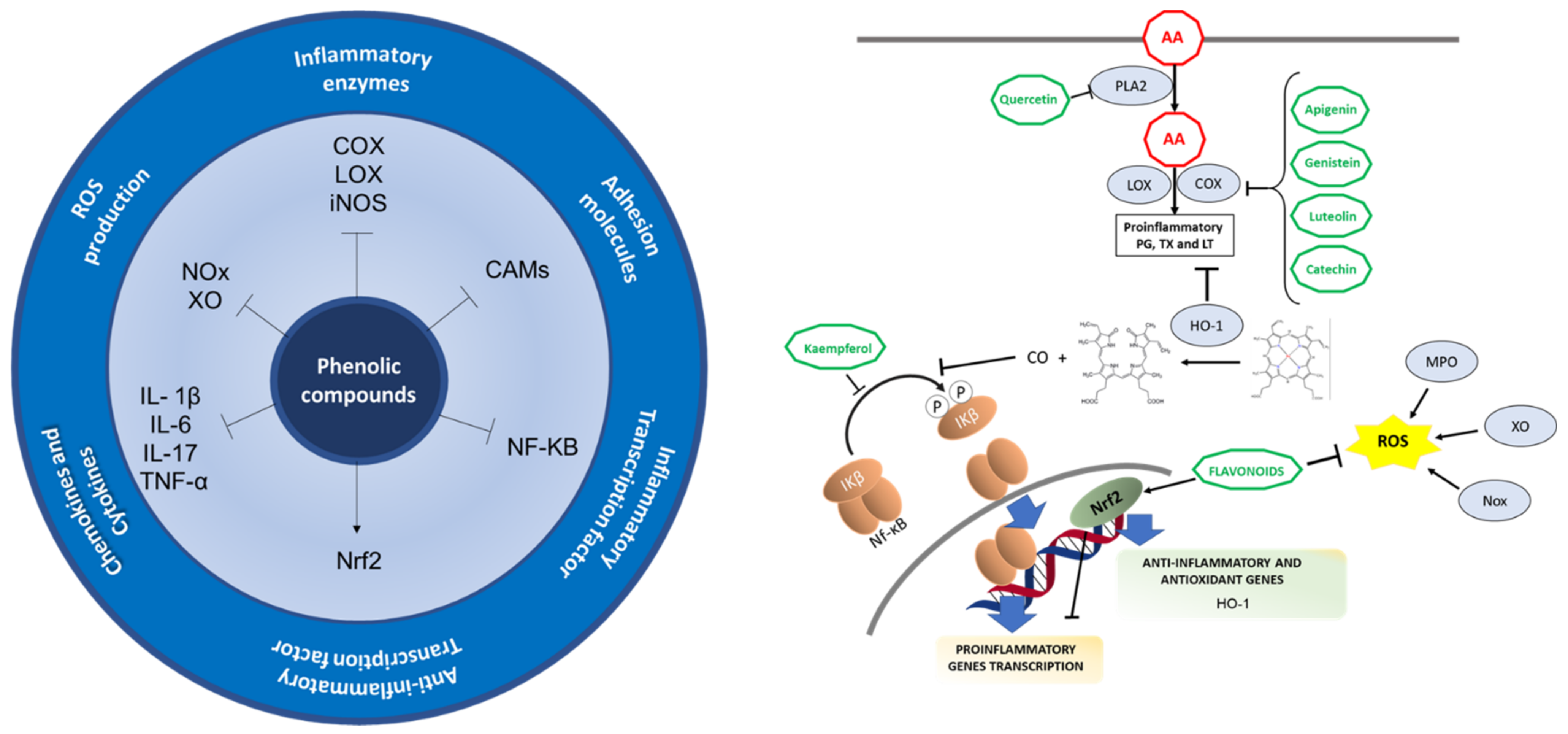
JoX | Free Full-Text | Antiviral and Anti-Inflammatory Plant-Derived Bioactive Compounds and Their Potential Use in the Treatment of COVID-19-Related Pathologies
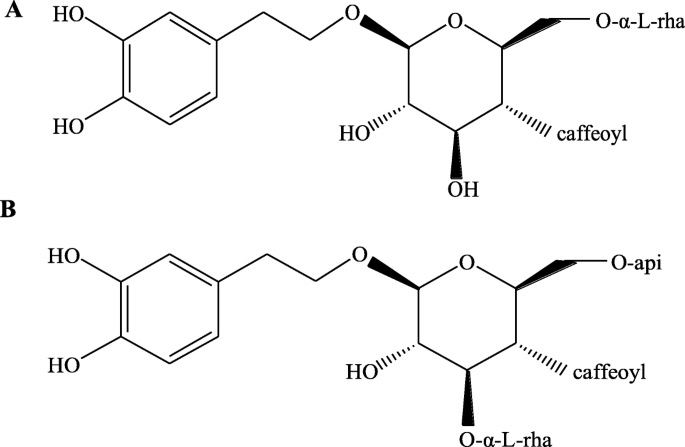
Exploration of anti-inflammatory mechanism of forsythiaside A and forsythiaside B in CuSO4-induced inflammation in zebrafish by metabolomic and proteomic analyses | Journal of Neuroinflammation | Full Text

Anti-inflammatory mechanism of lonchocarpine in LPS- or poly(I:C)-induced neuroinflammation - ScienceDirect

Is there a future for andrographolide to be an anti‐inflammatory drug? Deciphering its major mechanisms of action | Semantic Scholar
Mechanisms Involved in the Anti-Inflammatory Action of a Polysulfated Fraction from Gracilaria cornea in Rats | PLOS ONE

Anti-inflammatory Mechanism Involved in 4-Ethylguaiacol-Mediated Inhibition of LPS-Induced Inflammation in THP-1 Cells | Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry

Molecular mechanism of the anti-inflammatory effects of Sophorae Flavescentis Aiton identified by network pharmacology | Scientific Reports
The Anti-Inflammatory Effects and Mechanisms of Eupafolin in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Responses in RAW264.7 Macrophages | PLOS ONE
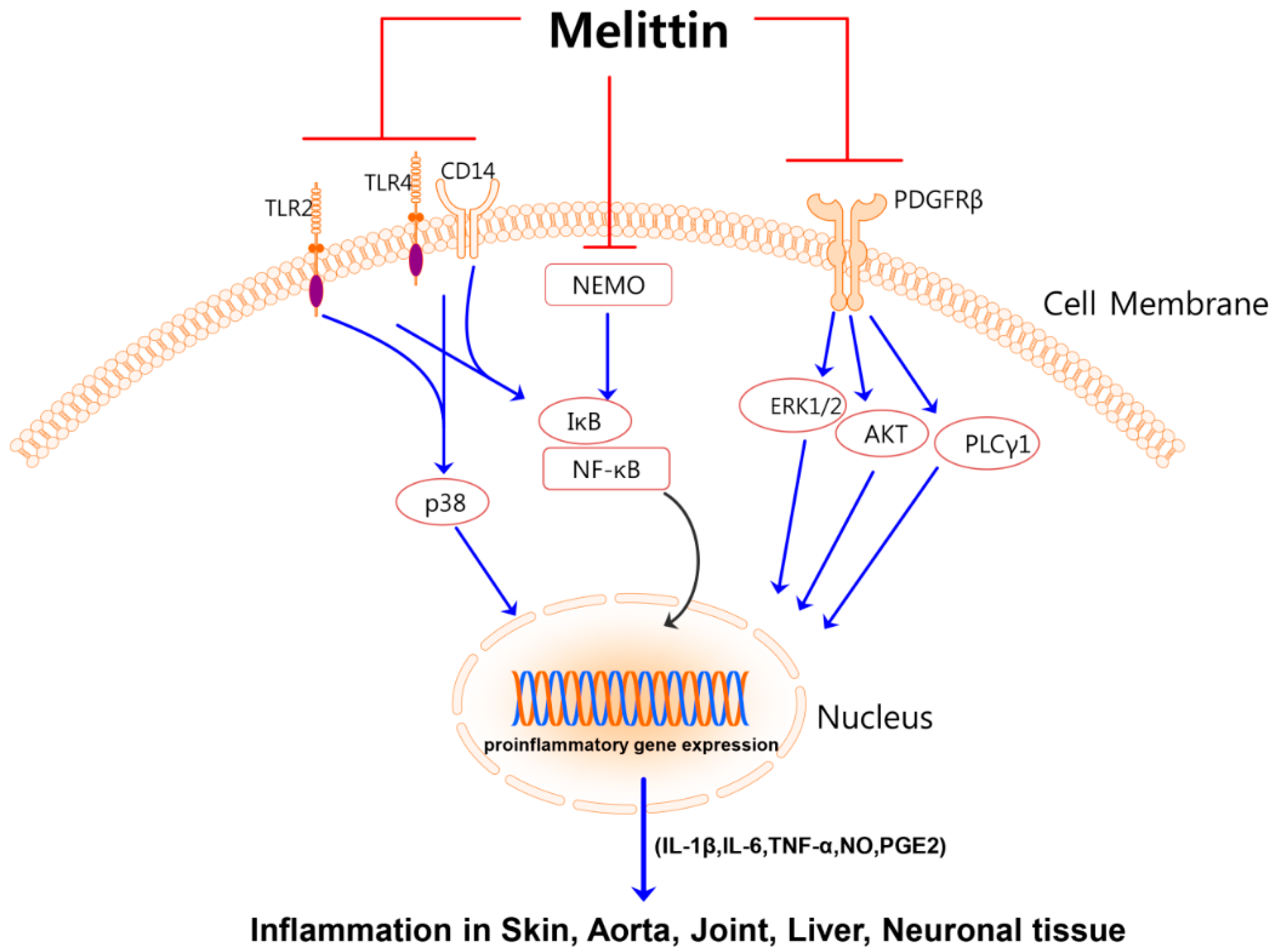
Molecules | Free Full-Text | Anti-Inflammatory Applications of Melittin, a Major Component of Bee Venom: Detailed Mechanism of Action and Adverse Effects
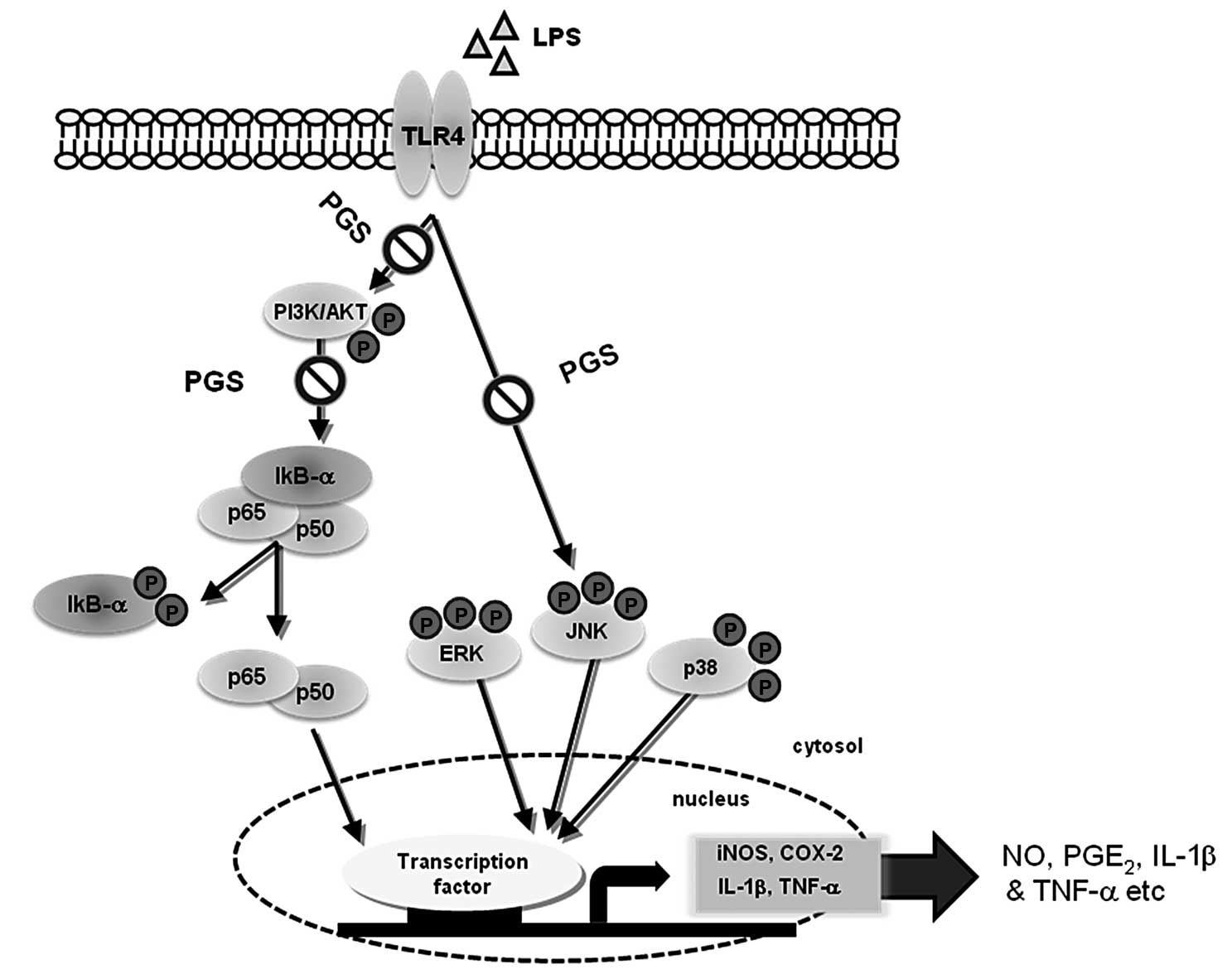
Anti-inflammatory effects of saponins derived from the roots of Platycodon grandiflorus in lipopolysaccharide‑stimulated BV2 microglial cells
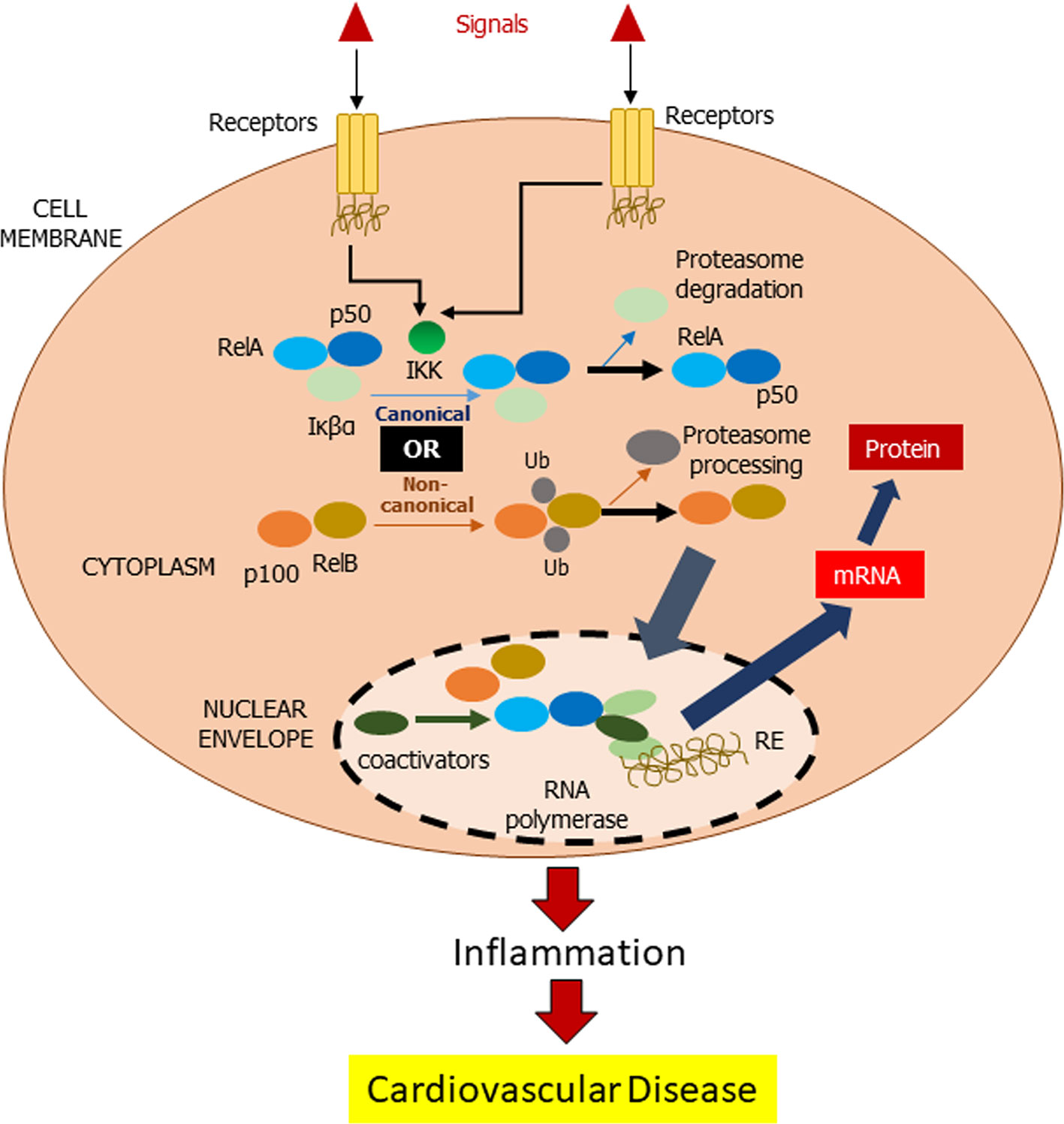
Frontiers | Flavonoids as Natural Anti-Inflammatory Agents Targeting Nuclear Factor-Kappa B (NFκB) Signaling in Cardiovascular Diseases: A Mini Review
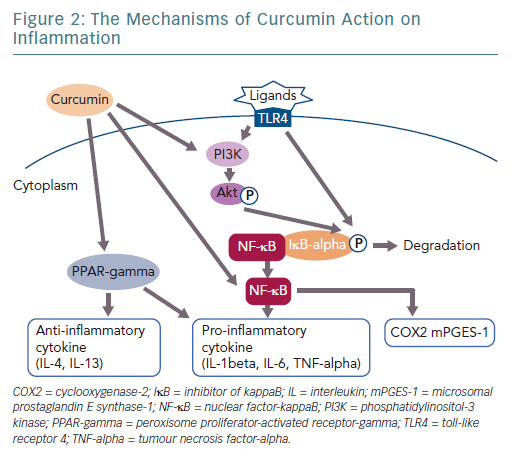
Anti-inflammatory Action of Curcumin and Its Use in the Treatment of Lifestyle-related Diseases | ECR Journal